The internet is a continuously evolving space. From its beginnings as a mostly static medium aka Web 1.0, it has now become a storehouse of user-generated content, or what we call Web 2.0
One thing has remained constant – the control that large corporations exert on what we can post and watch. It is this aspect of control over the internet that Web 3.0 promises to upend
While the concept behind Web 3.0 has its merits, there are still issues to be tackled before it gains universal acceptance

The internet is a continuously evolving space. From its beginnings as a mostly static medium aka Web 1.0, it has now become a storehouse of user-generated content, or what we call Web 2.0. So, what’s the next big wave that we should look out for?
We, the users, are increasingly contributing more and more of the information and content that drives the Internet. One thing has remained constant – the control that large corporations such as Google, Apple, Amazon, Meta, and Microsoft exert on what we can post and watch. It is this aspect of control over the internet that Web 3.0 promises to upend.
Power To The People
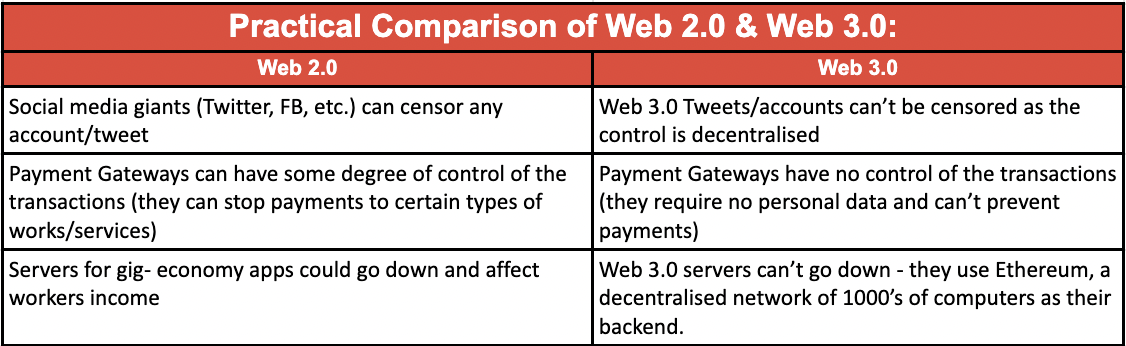
Anyone who has spent any amount of time on social media platforms would have realized how easy it is for large corporations to censor content that they find inconvenient. Or, for payment gateways to block entities based on their own, often subjective, parameters. So, the way the web currently works is to monetise the vast amounts of data that users generate but give the same users little control about how this data is used.
The driving principle behind Web 3.0 is to decentralise the way data is stored and used. Naturally, that promises to give users total control over what they upload online and how they protect their data and content.
Accountability Through Blockchain
At the heart of Web 3.0 is blockchain technology that ensures open infrastructure, security, and collaboration. Rather than depending on the whims and vested interests of technology giants, blockchain will ensure trust verification, including privacy protection, decentralised infrastructure and application platforms, and decentralised identities. By enabling the individual to be a sovereign, Web 3.0 promises to make the Internet a more equitable space.
Blockchain technologies like Ethereum make security and privacy key factors in how individuals control the data that they upload on the Internet. It incentives developers to create what is known as dApps or Decentralised Apps, as there is no chance of blockage or denial of service. In such a structure, payments are built-in via the native token – ether. Further, no permissions are needed to develop, provided users or developers are on the network. Dapps are also future-proofed, as Ethereum is a Turing Complete blockchain with the capability to understand and implement any future agreement, even those that have not been thought of yet.
Web 3.0 – Democratised Through Decentralisation
Another reason for Big Tech’s monopoly on online content is simple – centralized data storage. Web 1.0 placed the onus of data storage on the publisher, requiring content creators to maintain their own servers and distribution infrastructure.
Web 2.0 aimed to solve this issue by offering users unlimited storage space on social media platforms’ vast data farms, encouraging more and more users to create and upload content. Platforms often monetized this content, sometimes at the cost of user privacy. In the process, the platforms locked users into their ecosystem, making it difficult for them to have complete control over their data.
Web 3.0 removes this hurdle by offering a decentralised model of data storage and usage. Ethereum Blockchain technology gives users global access to a peer-to-peer network of nodes, where data is stored. These can be accessed by anyone to write on it, but never to update existing data. By not being owned by a single entity, control of the data is totally in the creator’s control, with full power to disseminate it as per his or her wish. Tokenisation of the data also means that ownership is clearly and irrevocably established, eliminating any disputes. And, finally, decentralisation means that the system has 100% runtime, as there is no single server that can crash and paralyse the system.
Is Web 3.0 Still A Work in Progress?
While the concept behind Web 3.0 has its merits, there are still issues to be tackled before it gains universal acceptance.
The first issue is compatibility with current web browsers, as none are compatible with Web 3.0 protocols. Further, widespread usage of blockchain technology is still to take off, with standards and protocols yet to be clearly defined. Scalability is also a challenge, as decentralisation makes transactions slower. Cost, too, becomes a factor as app developers find it expensive to put anything but small parts of their code on the blockchain.
Web 3.0 Limitations:
- Scalability: As transactions are decentralised the speed is slower.
- UX: Extra steps, software, and education are required for interaction in web 3.0; this might act as a hurdle for adoption
- Accessibility: the lack of integration in modern web browsers makes web 3.0 inaccessible to most users
- Cost: Most successful apps put very small portions of their code on the blockchain as it is very expensive
That said, there’s no denying that, as these issues get resolved, Web 3.0 is poised to make the Internet a more equitable, transparent, and secure space that encourages openness for everybody
The Impact on Content Creators And Game Developers
The industry leaders believe that the gaming, media, and entertainment industry, with its large numbers of creators and developers, will benefit most from the new world order defined by Web 3.0. With creators and developers getting full control over their content, they will lead the charge in Web 3.0 and must be supported by large M&E and gaming organisations.