The coaching world is crowded. There’s BetterUp, a re-skilling platform that wants to bring executive coaching to employees, and Sounding Board, which mixes SaaS and coaching services. Not to mention a slew of smaller yet ambitious startups like Mentor Collective, which matches students to mentors based on their backgrounds, Medley, which offers leadership courses, and Curious Cardinals, which helps younger students navigate higher ed.
So, do we really need another startup? If you ask John Koelliker, a former product manager at marketplaces including Uber and LinkedIn, the answer is obvious enough that he started a company.
Founded by Koelliker last year, Leland is taking on the coaching space with a focus on helping people navigate their careers — whether that is landing admissions to their dream business school or finally pivoting into the venture capital industry. The startup tells TC that it raised a $4 million seed round led by Contrary, and investors including Goodwater, FJ Labs, Next Play Ventures and executives from Koelliker’s previous employer, LinkedIn. Leland’s total known capital, to date, is $5.1 million.
Koelliker believes that Leland differs from other startups because of its targeted customer base. By working with an older demographic in search of career transitions, the startup avoids the tutoring space — and thus heavyweight companies like Wyzant and Varsity Tutors.
Along with the funding, Leland announced eight new coaching categories, growing past its initial focus on helping people get placement in MBA programs. Leland’s website now indicates that it offers coaches to help people take tests like the SAT, ACT, GMAT or GRE, as well as break into private equity, product management, investment banking and other tech fields.
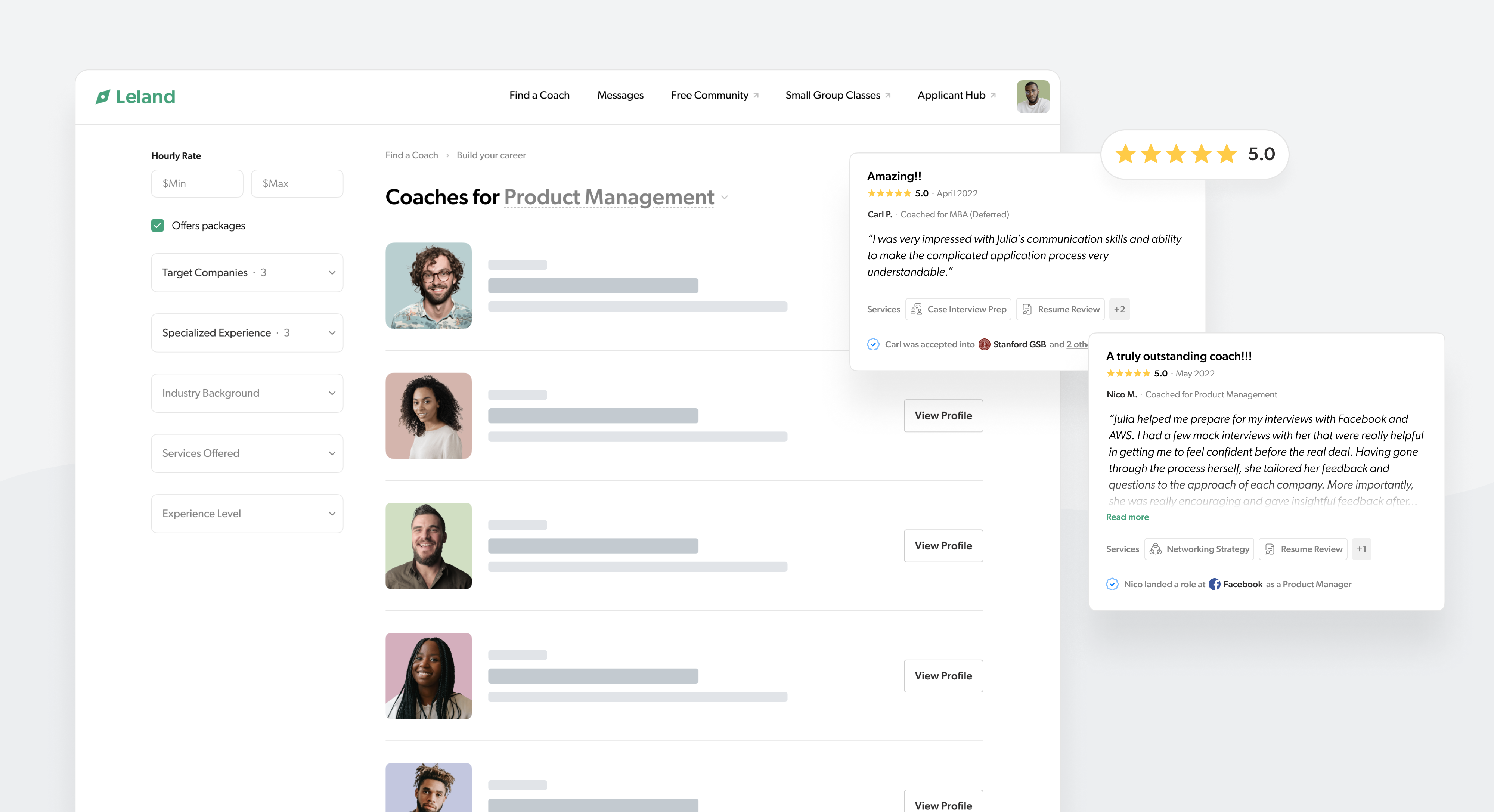
Image Credits: Leland
The company says that, in the last nine months, hundreds of customers have purchased more than 2,500 hours of coaching on Leland. Now that the focus is expanding, the clientele should as well.
Edtech has always been in search of a magic metric, or a way to quantify the balance it strikes between outcomes, engagement and actual comprehension. Sometimes, the best results can often be based on emotions, not actions, or change, not a test. Leland appears to be comfortable with striking a balance.
For example, people who sign up for Leland are told to share their goal outcome. “Instead of just saying, I’m going to be a life coach and help you, we’re going to connect you with someone who fits your budget, background and helps you get placed in that goal.” Now, the startup is careful not to guarantee placement — ahem, unlike some companies — because not every person who dreams up a spot in Stanford will get one.
“Maybe you can’t go to Stanford or maybe you can’t get into Google as a PM,” Koelliker said. “But everyone can reach a goal and so part of it is having coaches help them figure out what that goal is for them.”
About 70% of coaches use the income as a side hustle. Unlike companies like Maven or MasterClass, which require more buy-in from creators, Leland wants to be a lightweight way for passionate people to share what they know.
“You don’t have to have 100,000 followers on TikTok to be a creator or to be an expert or to be helpful to someone…that expertise is actually spread out into the minds of many,” he said. Leland wants to bring on creators who maybe don’t want to build a website or creator content, but instead want to talk shop and riff.
Coaches on the platform charge an hourly rate for their services that Leland says is much cheaper than traditional services. The startup charges transaction fees depending on how much a client pays a coach: For example, if a client pays a coach less than $1,000, Leland takes a 20% cut. If the total check is more than $10,000, Leland only takes a 10% fee.
Tech has tried to increase access to mentorship before, but always hits a clear challenge: demand is there, but serendipity — or the chasm between what makes someone an effective mentor versus just a speed dial for questions — is hard to scale.
For now, Koelliker thinks that focusing on consumers — instead of hungry enterprises — will help the company be more targeted and thus more efficacious. The startup monetized on day one, and while it hasn’t officially gone to market yet, that changes today.