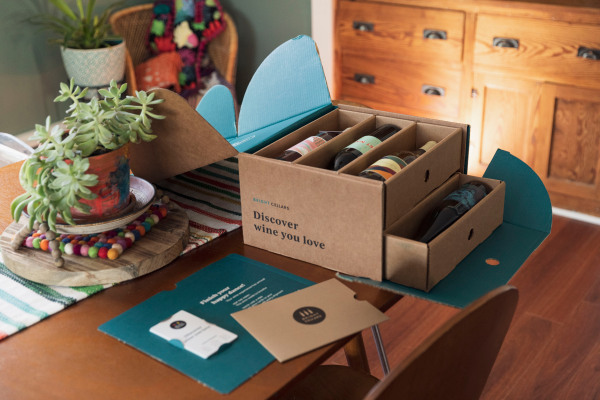
Bright Cellars, a six-year-old subscription-based wine seller has, like many upstarts, evolved over time. While it once sent its club members third-party wines that fit their particular profiles, Milwaukee, Wisconsin-based Bright Cellars says it’s now amassing enough data about its customers that it no longer sells wines made by other brands. Instead, while some of its “original” offerings are admittedly sold by other labels under different names, it is increasingly finding success by directing its winemaker partners to tweak the recipe, so to speak.
“We’re optimizing wine like you might optimize a more digital product,” says co-founder and CEO, Richard Yau, a San Francisco native whose startup entered into a regional accelerator program early on and stayed, though the company is now largely decentralized.
We talked earlier today with Yau about that shift, which investors are supporting with $11.2 million in Series B funding, led by Cleveland Avenue, with participation from earlier backers Revolution Ventures and Northwestern Mutual. (The company has now raised roughly $20 million altogether).
Yau also talked about industry trends that he’s seeing because of all that data collection.
TC: You’re building a portfolio of wines. What does that mean?
RY: We don’t own any land. We’re working primarily with suppliers [as do big companies like Gallo and Constellation], but at a larger scale than before, so we now get to shape what wines taste like and look like, and we can optimize across variables like how sweet should this wine be? How acidic? What do we want its color and brand and label to look like and which segment of our customers will really enjoy this wine the most?
TC: What’s one of your concoctions?
RY: We have a sparkling wine that’s produced in the Champagne method — not a Champagne wine; it’s a domestic wine — using grape varietals that no one uses for sparkling wine, and it’s one of the top-rated wines on our platform. Sparkling wine has been really good for us.
TC: How many subscribers do you have?
RY: We can’t share that, but we saw an acceleration in not just new subscribers throughout the pandemic but also in terms of seeing a larger share of [customers’] wallets going to D2C, and that impacted us pretty positively. Even as things eased up over the summer, we saw that people were cooking and eating at home more [and drinking wine].
TC: What’s the average price of a bottle of wine on the platform?
RY: $20 to $25.
TC: Where are your grape suppliers?
RY: A lot are on the West Coast, in Washington and California, but we also have grape suppliers internationally, including in South America and Europe.
TC: How many wines do you offer, and how long do you trial a wine?
RY: We’ve tested around 600, and at any given time, we’ll have 40 to 50 wines on the platform. We don’t stock everything forever; those that don’t do as well, we basically eliminate.
TC: A lot of D2C brands eventually branch into real-world locations. You aren’t doing that. Why not?
RY: It’s possible that we might at some point, but we like being D2C and it makes a lot of sense in a world where our members now work from home and are home to receive packages. It lines up with e-commerce trends in general. If you’re not buying your groceries at the store anymore, you aren’t buying wines at the store, either.
TC: From where are these bottles shipped?
RY: From a variety of places, but primarily from Santa Rosa [in the Bay Area].
TC: Have you seen the impact the weather is having on California winemakers, some of whom are now spraying sunscreen on their grapes to protect them?
RY: [Climate change] has certainly affected the wine industry. One of the fortunate things about us is we have flexibility in the suppliers we’re working with, so from a business-health perspective, we haven’t been as affected by that. Because a lot of our operations are in California, we did a couple of years ago have some interruptions with distribution where we weren’t able to ship some days; we were also impacted by warm temperatures. But fortunately, so far for this year, we haven’t had any operational or supply-chain disruptions.
TC: Have you been approached by one of legacy firms about a partnership or acquisition?
RY: We’ve had conversations, more in terms of partnerships because we have lots of data and can help them. For example, we can launch a new wine and get feedback almost like a focus group to figure out who likes what. We can split test two different blends for a wine and figure out which does better. That’s where conversations with legacy wine companies have happened.
TC: So they’d pay you for your data.
RY: We’re not opposed to selling data in the future, but we’ve approached it more like, here’s an opportunity to learn about how innovation works at a larger wine company. We don’t expect to be able to do what Constellation does well — with its large salesforce and distributors in every state — but what we can do in a complementary way is understand the consumer.
TC: What have you learned that might surprise outsiders?
RY: Petite sirah [offerings] do as well, if not better than, cabernet and pinot noir on the platform. Cab and pinot are fully 50 times the market size of petite sirah, but we see that our members really like it.
People also like merlot a lot more than they think — pretty much across all demographics. People like to hate merlot, but when we look at red blends that do well . . .
TC: What do people have against merlot?
RY: [Laughs.] Have you ever seen “Sideways?” That has something to do with it, still. Meanwhile, pinot noir remains popular, but people don’t like it as much as [other wine sellers] think.


![Read more about the article [Funding alert] Investment platform Stockal raises $3M in pre-Series A round](https://blog.digitalsevaa.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/Imageeon8-1620295026066-300x150.jpg)